A single-page website often struggles with SEO due to several limitations, such as the inability to target multiple keywords across separate pages, the lack of an internal linking structure, and slower loading times caused by heavy JavaScript. Google’s algorithms prioritize topic relevance and site hierarchy, which single-page sites inherently lack.
So, if you’ve been wondering why your site looks great but still doesn’t show up on Google the way you expected, this might be the reason.
“SEO, in a nutshell, is the art and science of pleasing search engines.”
— Neil Patel, globally recognized digital marketer
This means more than just inserting keywords; Google demands structured, easily navigable content, optimized URL structures, and fast load times. Unfortunately, many single-page websites (SPAs) fall short in these areas, which makes it harder for them to compete in organic search results.
How to know if you need a single-page or multi-page website?
A Single-Page Website, also known as a one-pager, is a type of website where all the content is presented on one continuous scrolling page. Instead of navigating to separate pages, users scroll to access different sections such as About, Services, and Contact. These sites are often built using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or modern web frameworks, and are designed to provide a smooth, streamlined user experience.

Key Characteristics:
- Single HTML page
- Long scrolling layout
- Minimal navigation
- Focus on a single idea or message
So, basically, you may prefer going for a “single-page” website if:
- You’ve a limited budget.
- You’re promoting one product or service and want to focus attention on that.
- You need a quick launch or temporary site, like for an event, webinar, or product drop.
- Your content is minimal and can fit neatly on one scrollable page.
- You’re running paid ad campaigns and need a focused landing page.
- You’re just building brand presence or testing an idea with limited content.
On the other hand, a Multi-Page Website is: A website that consists of multiple web pages linked together under a single domain. These pages are typically accessed through navigation menus, allowing users to explore different sections or content areas of the site. Unlike single-page websites, which display all content on a single page, multi-page sites break down information into separate, organized pages.
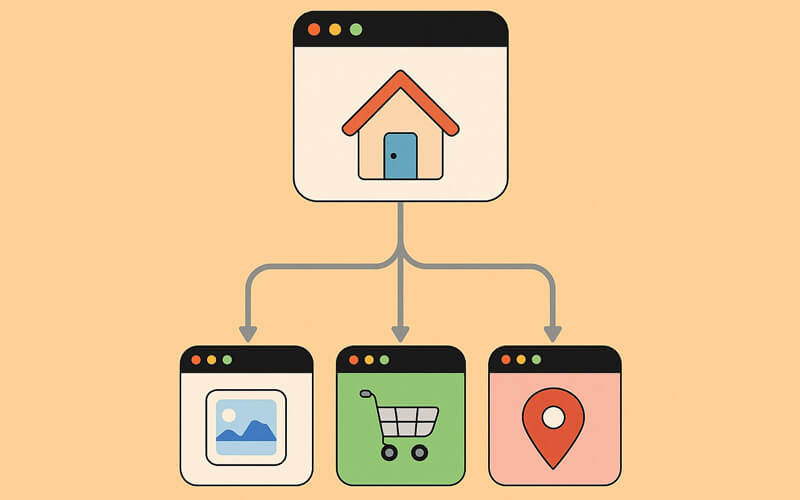
Key Characteristics:
- Multiple Pages
- Structured Navigation
- Scalability
- Detailed Content
- SEO Optimization
- Suitable for Diverse Needs
- Content Siloing
- Clear Hierarchy
Given this, a “multi-page website” might be the right choice for you when:
- You offer multiple services or products
- You want to rank for many different keywords
- Your business is expected to grow or expand
- You need advanced functionality
- You want clear, organized navigation
- You need separate landing pages for marketing or ads
- You want to build authority and trust
Confused about your best option? A Single-Page Website or Multi-page Website?
Talk to our experienced SEO team, and they’ll guide you toward the right choice using their specialized knowledge and expertise.
Reasons Why Single-Page Sites Struggle With SEO
Limited Keyword Targeting:
One Page, One Focus: A multi-page website allows each page to target a distinct set of keywords and topics. On a single-page site, you’re limited to optimizing for a very narrow range of keywords for the entire site. Trying to cram too many keywords onto one page can lead to “keyword dilution,” making it difficult for search engines to understand the primary focus of the page.
Less Depth for Specific Queries: Search engines prioritize content that thoroughly answers user queries. With all content on one page, it’s hard to dive deeply into specific subjects, which limits the site’s ability to rank for more niche or long-tail keywords.
Lack of Content Depth and Authority:
Thin Content: To avoid overwhelming users, single-page sites often have limited content. This lack of in-depth information can make it difficult for search engines to perceive the site as an authoritative source on any given topic.
Difficulty Building Topical Authority: A multi-page site can build authority across various related topics through dedicated pages and blog posts. A single-page site has a harder time demonstrating this breadth of knowledge.
Limited Internal Linking Opportunities:
SEO Value of Internal Links: Internal links help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your website, passing “link juice” between related pages and improving crawlability.
Non-existent Internal Linking: On a single-page site, all content is on one URL, so there are virtually no opportunities for internal linking. While anchor links can navigate within the page, they don’t carry the same SEO weight as links to separate, indexed pages.
Challenges with On-Page SEO Elements:
Single Meta Tags: You only get one set of meta titles and meta descriptions for the entire single-page site. This severely restricts your ability to tailor these crucial elements to different keywords and search intents.
H1 Limitations: While you can use multiple H2s, H3s, etc., there’s typically only one H1 for the entire page, further limiting distinct topic targeting.
URL Structure and Hierarchy:
One URL: A multi-page site benefits from a logical URL structure (e.g., yoursite.com/services/web-design) that clearly indicates content organization to search engines. Single-page sites typically have only one URL, making it harder for search engines to discern the different sections and their individual relevance.
Anchor Links vs. Separate URLs: While anchor links can create “sections,” they don’t function as distinct pages in terms of SEO. Search engines generally treat the entire single page as one entity.
Backlink Acquisition:
Fewer Linkable Assets: Multi-page sites, especially those with blog posts, detailed service pages, or in-depth resources, offer many opportunities for other websites to link to specific content. A single-page site has far fewer “linkable assets,” making it harder to naturally acquire valuable backlinks, which are a strong ranking factor.
User Experience (UX) Issues (that indirectly impact SEO):
Potentially Slower Load Times: If a single-page site tries to cram too much content, high-resolution images, videos, and scripts onto one page, it can lead to slower loading times. Page speed is a ranking factor, and slow sites can increase bounce rates, signaling a poor user experience to search engines.
Difficulty in Navigation: While scrolling can be intuitive, for very long single-page sites, users might find it challenging to quickly locate specific information, leading to frustration and higher bounce rates.
Limited Analytics Tracking: It can be more challenging to track specific user behavior and engagement on a single-page site compared to a multi-page site where you can track page views, conversion paths, and time spent on individual pages.
A Single-Page Vs Multi-Page Website:
The choice between a single and a multi-page website isn’t always straightforward, as each offers unique benefits and limitations. To simplify this critical decision, we’ve compiled a comprehensive comparison.
For your convenience, we present a comparative table that highlights the essential differences between both types of websites:
| Feature / Aspect | Single-Page Website | Multi-Page Website |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All content resides on one HTML page; navigation involves scrolling or jumping to sections. | Multiple distinct HTML pages linked together; navigation involves loading new pages. |
| User Experience (UX) | Seamless, linear, and intuitive scrolling. Great for storytelling and guiding users to a single call to action. | Structured and organized; easier for users to find specific information and content. |
| UX Drawbacks | Can become overwhelming with too much content. Harder to share/bookmark individual sections. | More page reloads; slower perceived speed if not optimized well. |
| SEO Potential | Limited keyword targeting and authority building. | Better for broad keyword targeting and internal linking. |
| Scalability | Harder to scale with new services or products. | Highly scalable; easier to expand site structure. |
Single-Page vs Multi-Page Website Examples

Single-Page vs Multi-page Website Pros and Cons
Single-Page Website
Pros:
- Fast to design and develop
- Smooth, guided user experience
- Great for mobile and scrolling
- Easier to focus on one goal (e.g., conversions)
- Often loads faster (if optimized)
Cons:
- Limited SEO opportunities
- Not ideal for complex content
- Can become heavy if too much is crammed
- Harder to scale later
- Analytics are less detailed (fewer pages to track)
Multi-Page Website
Pros:
- Better for SEO (more keywords, pages)
- Easy to organize lots of content
- Scalable for future growth
- Better user navigation for diverse topics
- More detailed analytics possible
Cons:
- Takes longer to build
- Can overwhelm users if poorly structured
- Slower load times if not optimized
- Navigation may require more effort
- Needs regular content maintenance
To know more about our SEO services or for any other queries
What to Do if You Have a Single-Page Website?
1. Optimize Your Core Content & Headings for Clarity and Focus
Google emphasizes clear, well-organized, and valuable content. For a single-page site, this means:
- One Primary Topic/Purpose: Since you only have one page, determine the single, most important overall purpose or primary topic of your website. This should be reflected in your main H1 heading and your overall site’s title tag and meta description.
- Title Tag (<title>): Craft a compelling and descriptive title tag (under 60 characters) that includes your primary keyword(s) and accurately represents the entire page’s content.
- Meta Description: Write a concise and persuasive meta description (around 150-160 characters) that highlights the value of your content and encourages clicks. It should provide a summary of the whole page.
- Logical Heading Structure (H1, H2, H3):
- Use only one H1 for the main heading of the entire page.
- Use H2s to logically separate distinct sections of your content (e.g., “Our Services,” “About Us,” “Portfolio,” “Contact Us”). Think of these as sub-topics.
- Use H3s and beyond for further sub-sections within your H2s.
- Strategic Keyword Placement: Naturally integrate keywords relevant to each section within its respective heading and body text. Avoid keyword stuffing, as Google penalizes this. Focus on providing helpful, well-written content that answers user queries naturally.
- Content Quality and Depth: While space is limited, ensure the content on each section is high-quality, informative, and as comprehensive as possible without overwhelming the user. Google values content that demonstrates expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
ALSO CHECK THIS: Google’s Creating Helpful, Reliable, People-First Content Guide
2. Leverage URL Fragments (Anchor Links) and Structured Data
- Descriptive Anchor Links: Use clear, semantic anchor links for your internal navigation (e.g., yourdomain.com/#services, yourdomain.com/#about). The anchor text should accurately describe the section it links to. This improves user experience and can give Google more context about each section.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Implement schema markup (e.g., Organization, Product, Service, LocalBusiness, FAQPage) to provide Google with explicit information about your content. This can lead to rich snippets in search results, increasing visibility. For a single-page site, apply a schema that best describes the entire entity represented by the page.
3. Prioritize Technical SEO Fundamentals

These aspects are critical for any website, including single-page sites, as they directly impact crawlability, indexing, and user experience.
- Page Speed (Core Web Vitals): This is paramount for single-page sites because all assets (images, scripts, CSS) often load initially.
- Optimize Images: Compress images, use modern formats (WebP), and implement lazy loading for images below the fold.
- Minify Code: Reduce the size of your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Configure your server to allow browsers to cache static assets.
- Consider Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or Prerendering for SPAs: If your single-page site is a JavaScript-heavy Single Page Application (SPA), server-side rendering or prerendering tools can send a fully rendered HTML page to Googlebot, ensuring all content is crawlable. This is often recommended by Google for complex SPAs.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your site is fully responsive and provides an excellent user experience on all devices. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your content for indexing and ranking.
- Secure (HTTPS): Use HTTPS. It’s a fundamental security measure and a minor ranking signal.
- XML Sitemap: While you have one URL, submitting an XML sitemap to Google Search Console is still a good practice. It confirms to Google the URLs you want indexed.
- Robots.txt: Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow Googlebot to crawl all necessary resources (CSS, JS, images) and the main page.

4. Enhance User Experience (UX)
Google heavily emphasizes user experience. A good UX can lead to higher engagement, lower bounce rates, and ultimately, better rankings.
- Clear Navigation: Despite being one page, ensure there’s a clear and intuitive sticky navigation menu that uses anchor links to jump to relevant sections.
- Visual Appeal and Readability: Use good design, contrasting colors, and legible fonts. Break up long blocks of text with images, videos, and bullet points to improve readability.
- Calls to Action (CTAs): Place clear and prominent CTAs where appropriate to guide users towards desired actions.
- Accessibility: Ensure your site is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.

5. Build Quality Backlinks
Backlinks from reputable sources remain a strong ranking factor for Google.
- Create Link-Worthy Content: Despite being a single page, ensure your content is valuable enough that other websites will want to link to it. This could be a unique tool, a compelling story, original research, or an excellent resource.
- Outreach: Actively promote your website and its unique value proposition to relevant websites, industry influencers, and directories to earn natural backlinks.
6. Monitor and Iterate with Google Search Console & Analytics
Google Search Console
This is your primary tool for monitoring your single-page site’s performance on Google.
- Index Coverage Report: Check if your page is being indexed correctly.
- Performance Report: Monitor impressions, clicks, CTR, and average position for your target keywords.
- Core Web Vitals Report: Identify and fix page speed issues.
- Mobile Usability Report: Ensure your site is mobile-friendly.
- URL Inspection Tool: Use this to see how Google crawls and renders your page.
Google Analytics
- Track user behavior on your single page (e.g., scroll depth, time on page, engagement with different sections, conversions).
- For SPAs, ensure your analytics setup correctly tracks “virtual page views” as users navigate through sections using anchor links, so you can measure engagement with different content areas.
Important Considerations from Google’s Perspective:
- No “Magic Bullet”: There’s no secret trick for single-page sites. All fundamental SEO principles still apply.
- Focus on the User: Google’s algorithms are designed to serve the most helpful and relevant content to users. If your single-page site genuinely serves its users well, it has a better chance of ranking.
- Think About Scalability: If your business or content needs grow significantly, a multi-page site might eventually become more advantageous for long-term SEO scalability, allowing you to target a broader range of keywords and build deeper topical authority.
Final Takeaway
While single-page websites offer simplicity and speed, they do come with limitations, especially when it comes to SEO. The good news? You don’t need to scrap your site. With strategic keyword placement, technical enhancements, and layout optimization, your one-pager can still compete in search results. But if you’re ready to scale or target multiple topics, migrating to a multi-page structure could unlock far greater visibility and growth.
FAQs
- Are single-page websites bad for SEO?
Not inherently “bad,” but they present unique SEO challenges. They limit your ability to target a wide range of keywords, build deep topical authority, and leverage extensive internal linking, which can hinder organic visibility. - Are single-page applications bad for SEO?
SPAs can be challenging for SEO if not properly implemented. Googlebot needs to render JavaScript to see all content; without server-side rendering (SSR) or prerendering, important content might be missed, harming indexability and ranking. - How to do SEO for a one-page website?
Focus on a single, clear primary keyword for the entire page’s H1 and title tag. Use H2s for distinct sections, optimize page speed, ensure mobile-friendliness, and attract high-quality backlinks to boost authority for that core topic. - How do you improve SEO for a personal website?
Define your unique niche and target audience. Create high-quality, relevant content (even if concise), optimize for specific personal brand or portfolio keywords, ensure fast loading and mobile responsiveness, and actively seek backlinks from relevant sources. - How much does it harm SEO to have just a one-page website?
It doesn’t “harm” in a penalty sense, but it significantly limits your SEO potential. You’ll struggle to rank for diverse long-tail keywords, establish comprehensive topical authority, and benefit from the granular internal linking structure of multi-page sites. - How to SEO a Single-Page website
Maximize your single H1 and title tag with your core keyword. Use clear H2s to section content, ensure lightning-fast load times and mobile optimization. Implement descriptive anchor links for navigation and focus on building quality backlinks to the main URL.
Strengthen Your Website’s SEO with Ingenious Netsoft!
With over 15 years of experience, as one of the best SEO companies in USA, Ingenious Netsoft takes pride in offering result-oriented SEO services in USA, helping businesses of all scales make the most of their digital presence.
No matter if you’re working with a single-page site or planning to scale, we provide tailored SEO, SMO, and digital marketing services in USA to help you grow faster.
We’re ready to discuss your unique challenges and outline a path to digital success. Get started with a free quote now!